The total number of colonies is determined to determine the degree of contamination of the food by the bacteria and its hygienic quality. This method can also be used to observe the nature of the bacteria in the food and the dynamics of the bacteria in the food for hygienic evaluation of the sample to be tested. Provide scientific evidence. At present, the total number of colonies is a mandatory item in all kinds of food and sanitary bacteriological tests.
First, the definition of the total number of colonies

The total number of colonies refers to the total number of bacterial colonies grown per gram (per milliliter) of samples under certain conditions (such as aerobic conditions, nutrient conditions, pH, culture temperature and time). According to the national standard method, the total number of bacterial colonies that can grow on common nutrient agar plates under aerobic conditions at 37 ° C for 48 h, so anaerobic or microaerobic bacteria, special nutritional requirements and non-mesophilic Bacteria, because the existing conditions can not meet their physiological needs, it is difficult to breed and grow. Therefore, the total number of colonies does not indicate the total number of bacteria in the actual, and the total number of colonies cannot distinguish the types of bacteria therein, so it is sometimes referred to as the number of bacteria, the number of aerobic bacteria, and the like. The total number of colonies is used to determine the degree of contamination of the food by the bacteria and the quality of the hygiene. It reflects whether the food meets the hygiene requirements in the production process in order to make an appropriate hygienic evaluation of the sample to be tested. The total number of colonies indicates the quality of food hygiene to a certain extent.
Second, the sampling of the cake
When the sample is collected, 200 g of different parts of the sample are taken with a sterile tweezers, placed in a sterilization container, and taken immediately after being taken. The specific time should be delivered to the laboratory within 2 hours.

Third, the determination of the total number of colonies in the cake
1. Preparation and sterilization of the medium
4.5% nutrient agar and 0.85% sodium chloride solution were prepared and placed in a 300 ml flask and tube for autoclaving for 20 minutes. A 75% alcohol cotton ball was prepared as a reagent for testing the total number of colonies. The scale pipette and the culture dish should be thoroughly cleaned, and no bacteriostatic substances remain. After the dressing, it is sterilized for 15 minutes. After the reagent is sterilized, it is best to use it on the same day. Otherwise, the sterilization time should be increased for 5-10 minutes, and placed in the refrigerator at 0-4 °C for use. In order to ensure the complete sterility of the inspection process, the top of the graduated straw should be stuffed with cotton wool and then sterilized.
2. Pre-treatment of the laboratory
After the UV lamp is turned on for 30 minutes, it will be closed for 30 minutes before entering the laboratory for inspection. The nutrient agar is preheated in the water bath and can be used after it has not solidified. In order to ensure the accuracy of the test results, the microbiological laboratory is within two people.
3. Pretreatment of the sample
After entering the sterile room, first turn on the alcohol lamp, wipe the test hand and sample outer packaging with alcohol cotton ball. If it is the original packaging, use the sterile tweezers to clamp the wrapping paper, take the external and central part 25g, add 225ml sterile saline. In the middle, it is best to treat the homogenizer at a speed of 8000-10000r/min for 1min to make a 1:10 uniform dilution solution, use a 1ml sterile pipette to absorb 1ml of 1:10 dilution, and slowly inject 9ml along the tube wall. Sterilize the test tube with sterile saline or other dilute solution (note that the tip of the pipette does not touch the dilution in the tube). Shake the tube and mix well to make a 1:100 dilution. Another 1ml sterile pipette is taken, and the 10-fold incremental dilution is performed according to the above operation sequence, so that each increment is replaced by a 1ml sterile pipette.
4, inoculation, cultivation
When measuring the total number of bacteria, according to the requirements of the cake hygiene standard GB7099-2003 or the estimation of the contamination of the specimen, select 2-3 suitable dilutions, respectively, while doing 10 times incremental dilution, that is, to absorb 1 ml of the dilution pipette. The dilutions were placed in a sterilized dish and two plates were made as a parallel sample for each dilution. After the diluent is transferred into the plate, it should be poured into a plate of about 15ml in a nutrient agar medium (which can be placed in a 46±1°C water bath) and cooled to 46°C in a timely manner (15-20 minutes in winter and 30-35 minutes in summer). Rotate the plate to mix evenly. At the same time, the nutrient agar medium was poured into a sterilized blank plate as a blank control. After the agar has solidified, do not place it for a long time. The plate should be turned over and placed in a 36±1°C incubator for 48±2 hours. In order to control the pollution, at the same time as the sampling is carried out, an agar plate is opened on the workbench, and the exposure time should be from the time when the sample is prepared and diluted to the longest time when the plate is added, and then the inspection is performed. The plates are placed in a thermostat at the same time to understand whether the samples are contaminated during the inspection operation. Since the cakes after standing are like colonies, in order to determine whether or not the colonies are in the sample, at the same time as the sampling test, a plate can be made according to the selected dilution, and it is placed in an environment of about 0-4 °C until the result is observed. When doing a comparison.
5, the results report
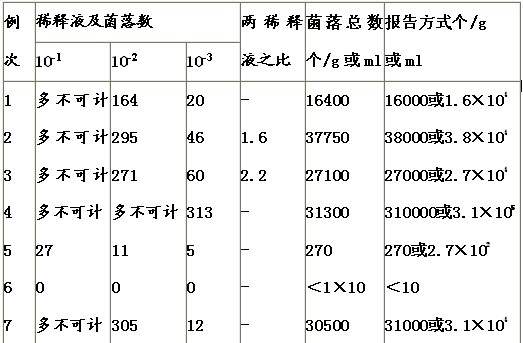
When reporting the total number of colonies, the dilution of the average number of colonies between 30-300 should be selected by multiplying the dilution factor. If the average number of colonies in all dilutions is not between 30 and 300, and some of them are greater than 300 or less than 30, Multiply the number of average colonies closest to 30 or 300 by the dilution factor. If there are two dilutions, the number of growth colonies is between 30-300, then the ratio of the two is determined. If the ratio is less than or equal to 2, the average should be reported; if greater than 2, the smaller number is reported (see Tables 2 and 3). When the number of colonies is less than 100, the actual number is reported. When the number of colonies is greater than 100, two significant figures are taken, and the values ​​after the two significant digits are rounded off. In order to shorten the number of zeros after the number, it can also be expressed by an index of 10 (see Table 1 "Report Mode" column). Note that the specified incubation time should be counted immediately. If it is not possible to count immediately, the plate should be present at 0-4 ° C, but not more than 24 h. If the plate has larger flaky colonies, it should not be used, but the plate without flaky colony growth should be the number of colonies of the dilution. If the flaky colony is less than half of the plate and the colony distribution is very uniform in the remaining half, calculate the half plate and multiply by 2 to represent the total number of colonies. The result of this test is that the dilution of 10-1 is uncountable, the dilution of 10-2 is 287, the dilution of 10-3 is 55, the ratio of two dilutions is 1.9, and the total number of colonies is the sum of two dilutions divided by two. Calculated as 41850, the reporting method is 42000 or 4.2×104.
Table 1 Dilution selection and colony number reporting method
Several issues that should be noted:
(1) The operation should be fast and accurate, including sampling, sample loading, injection of medium, and the like.
(2) When the sample is taken, it should be aseptically operated and promptly sent for inspection.
(3) The reagents used should be sterilized thoroughly and used as soon as possible.
(4) When the sample is diluted, it must be mixed evenly.
(5) Strict aseptic operation before and after injecting the medium.
(6) Note that the medium temperature is appropriate and the medium is thin and uniform.
(7) There must be a blank control in each test.
(8) The microbiological test shall not exceed two persons.
(9) The culture should be carried out quickly after the test.
(10) After the test is completed, the microorganisms are also sterilized by ultraviolet rays.
In short, in order to ensure the accuracy of the test results, in the total number of cake colonies, attention should be paid to the "details". Otherwise, the test results will have provenance, especially the results of the standard limits, which will often result in the judgment of the company's life and death due to our operational methods.
Household Gas Cylinder
Complete size and reliable quality of LPG Cylinders have gain our company good reputation.We are manufacturer and supplier of Gas Cylinder following your specific requirement. At the same time, we can according to your design to produce the valve for your request.
Gas Cylinders Advantages:
1.Experienced: Have adult management system and QC system
2.Discount: we will give our long term customers more discount
3.Any color or printing is OK
4.The material is recyclable, it`s environment-friendly
5.OEM is welcomed

Big Gas Cylinder, Welding Gas Cylinder, LPG Gas Tank, Gas Cylinder.
ANSUN IMPORT AND EXPORT LIMITED. , http://www.ansungroup.com